Understanding Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome (ZES) is a complex and rare condition that primarily affects the gastrointestinal system. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of ZES, including its symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and its association with multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN 1).
What is Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome?
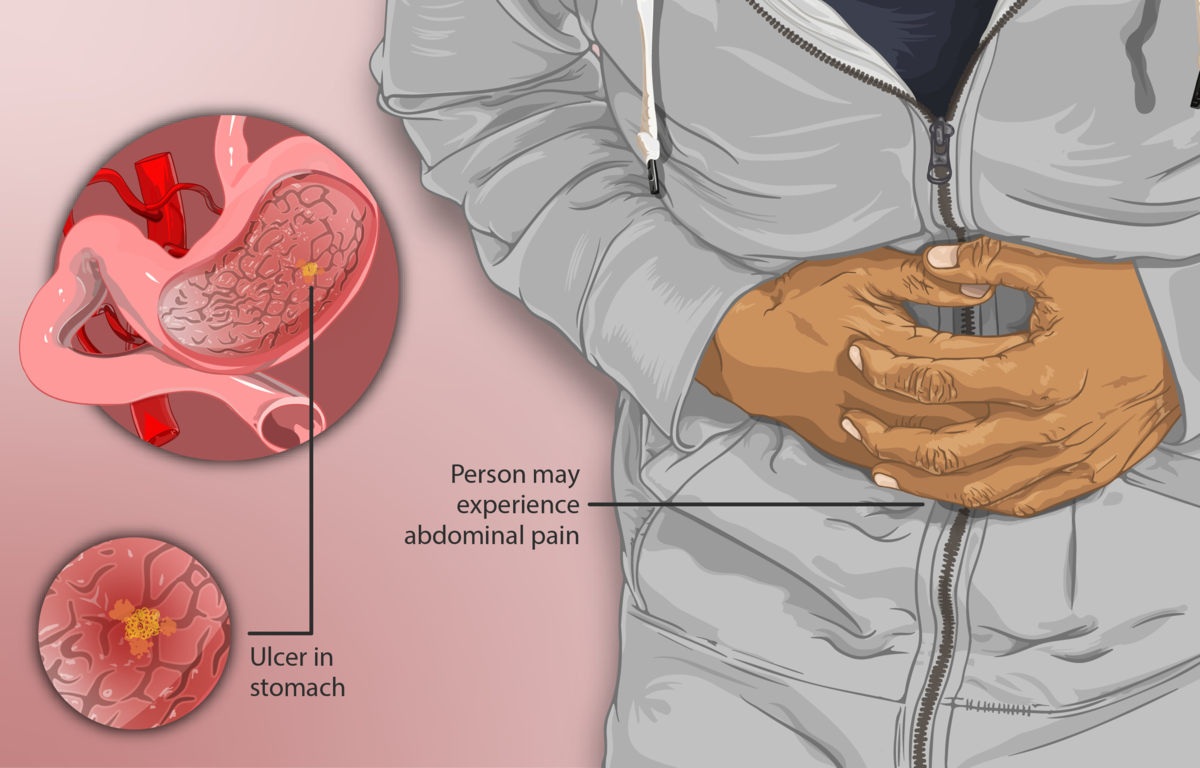
Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome is characterized by one or more tumors, known as gastrinomas, that develop in the pancreas or the duodenum (the first section of the small intestine). These tumors secrete excessive amounts of gastrin, a hormone that prompts the stomach to produce large amounts of acid. This overproduction often leads to peptic ulcers and other gastrointestinal complications.
Primary Features of ZES
- Excessive Gastric Acid Production: The hallmark of ZES is the overproduction of gastric acid, leading to peptic ulcers.
- Tumors (Gastrinomas): These can be benign or malignant, and are often difficult to detect due to their small size.
- Association with MEN 1: Approximately 25% of ZES cases are part of multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1, a condition involving tumors in multiple endocrine glands.
Epidemiology and Demographics
ZES is an extremely rare condition. It is slightly more prevalent in specific age groups, particularly among individuals aged 20 to 50 years. Gender-wise, there is a slight male predominance.
Causes and Risk Factors
The primary cause of ZES is the development of gastrinomas. These tumors trigger an increase in gastrin, a hormone that controls stomach acid production, leading to hypersecretion. Some cases are associated with Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia type 1 (MEN1), a genetic condition, underscoring the importance of genetic assessment in at-risk individuals. Understanding these causes and risk factors is essential for targeted treatment and management of ZES.
Symptoms of Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome
ZES symptoms are often mistaken for those of more common gastrointestinal disorders. The primary symptoms include:
- Abdominal Pain: The most common symptom, often resembling peptic ulcer pain.
- Diarrhea: Occurs in about 73% of patients, particularly those with MEN 1/ZES.
- Heartburn and Acid Reflux: Mimicking gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
- Nausea and Vomiting: Frequent occurrences due to high acid levels.
- Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Often due to ulceration, and may be the first presenting symptom.
- Weight Loss: A consequence of reduced nutrient absorption and appetite.
Patients may also exhibit symptoms related to MEN 1, such as kidney stones (nephrolithiasis), high calcium levels (hypercalcemia), and pituitary gland disorders.
Diagnosing Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome
Diagnosis of ZES involves a combination of clinical assessment, laboratory tests, and imaging studies:
- Blood Tests: Elevated gastrin levels in the blood are indicative of ZES.
- Upper Gastrointestinal Endoscopy: To examine the stomach and duodenum for ulcers and gastrinomas.
- Imaging Techniques: Ultrasound, CT scans, MRI, and nuclear scans are used to locate tumors.
- Endoscopic Ultrasound: Offers detailed imaging of the digestive tract, aiding in the detection of small tumors.
Treatment Strategies for Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome
Treatment focuses on managing the tumors and the ulcers:
Managing the Tumors
- Surgical Removal: If feasible, especially for solitary tumors.
- Debulking: Reducing the size of liver tumors.
- Embolization and Radiofrequency Ablation: To destroy tumor cells.
- Chemotherapy: For slowing tumor growth.
- Medications: For symptom relief and reducing tumor growth.
Managing the Ulcers
- Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs): Such as Omeprazole, Lansoprazole, Esomeprazole, and Rabeprazole, to reduce acid production.
- Acid Blockers: Less effective than PPIs but used in some cases.
- Surgery: To treat complications like bleeding ulcers, obstructions, or perforations.
Living with Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome
Living with ZES requires ongoing medical care and lifestyle adjustments. Patients are advised to:
- Monitor for Symptoms: Regular check-ups are crucial for early detection of changes or complications.
- Adhere to Medications: Consistent use of prescribed medications is essential for managing symptoms.
- Dietary Adjustments: Avoiding foods that trigger acid production can be helpful.
Conclusion
Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome is a rare but manageable condition. With proper medical care, individuals with ZES can lead a relatively normal life. Understanding the symptoms, staying vigilant about changes, and adhering to treatment plans are key to effective management.
If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms suggestive of ZES, consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and appropriate treatment. Remember, early diagnosis and intervention can significantly improve the quality of life for those living with Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome.
References
- Cho MS, Kasi A. Zollinger Ellison Syndrome. InStatPearls [Internet] 2022 Nov 21. StatPearls Publishing.
- Cingam SR, Botejue M, Hoilat GJ, Karanchi H. StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island (FL): Jul 28, 2023. Gastrinoma.
- Krampitz GW, Norton JA. Current management of the Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. Adv Surg. 2013;47:59-79.


